Nuclear Medicine
Introduction to Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is a clinical discipline that deals with ‘open’ sources of radiopharmaceuticals (radioisotope labelled with pharmaceutical agents) for various diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The radioactive component or ‘tracer’ is the emitter of radiation, which is used for detection in diagnostic application and for limited or restricted non-radioisotope component acts as the vehicle, which carries the radioactive nucleus to the cell, organ or the system that is targeted.
Nuclear Medicine deals with functional and metabolic imaging. Anatomical and function images of an organ system are complimentary to each other. Hybrid or fusion imaging offers both morphological & functional details of any abnormality related to any disease process.
SPECT-CT & PET-CT are different fusion imaging modalities offering morphological as well as functional metabolic details (Hybrid Imaging).
PET-CT SCAN
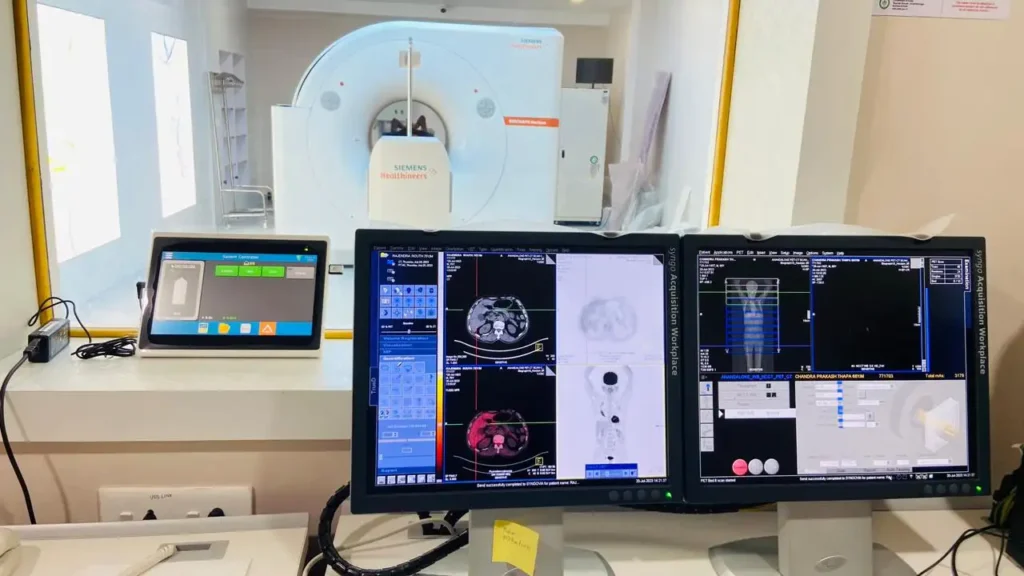
18-F-Fluoro Deoxy Glucose (FDG) PET:
- Diagnosis of Cancer
- Metastasis from unknown primary
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- to differentiate between Benign vs Malignant tumor
- Determination of Biopsy site.
- Metastatic vs Non-metastatic
- Metabolically most active part (Representative site) of the tumor.
- Staging
- Treatment response evaluation (Post chemo therapy and radiation therapy)
- Restaging in case of recurrence and defaulted patient.
- Follow up and long term evaluation
68-Gallium- DOTA PET:
- Neuroendocrine Tumour
- Medullary Carcinoma of Thyroid
68-Gallium/ 18 Fluorine- PSMA PET:
- Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Suspected recurrence in operated high grade Gliomas
SPECT (Gamma Camera)
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Stress/ Rest Thallium Scan
- To evaluate chest pain, to diagnose coronary artery disease.
- To assess severity and extent of ischemia and risk of infarction
- To assess myocardial viability in segments with wall motion abnormality.
- Suspected CAD in long standing diabetic patients
- Cardiac evaluation in high risk non-cardiac surgery and higher risk / high responsibility jobs.
MUGA SCAN
- For accurate assessment of LV function & Ejection Fraction (Gold standard for LVEF Assessment).
Lung Ventilation Perfusion Scan
- To diagnose pulmonary Thrombo-embolism.
Venography
- To diagnose deep vein thrombosis
GASTRO-ENTEROLOGY
Hepatobiliary Scan
- To diagnose acute cholecystitis and acalculous cholecystitis.
- To assess GB dysfunction.
- To study bile drainage, biliary atresia, bile leaks.
Liver & Spleen Sulphur Colloid Scan
- To evaluate cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
- Buddchiari, nodular hyperplasia & tumors
Blood Pool Scan (Tc – 99m RBCs)
- Hemangioma of liver
- GI Bleeding
- Tc- 99m Pertechnetate Meckel’s Diverticulum (for ectopic gastric mucosa)
GIT Luminal Studies
- Oesophageal transit study in dysphagia
- GE Reflux scintigraphy, Gastroparesis, post-operative status, dysmotility etc.
- Colorectal transit time for chronic constipation and suspected obstruction
WHOLE BODY MDP BONE SCAN
- Best available technique of survey for skeletal metastasis in patients with known or suspected cancer
- Osteogenic Sarcoma and Ewing’s tumor
- Assessment of metabolic bone disease.
- Evaluation of orthopedic problems like osteoid osteoma. Paget’s Disease etc.
- Langerhans’s Cell Histiocytosis (LCH).
- Multiple Myeloma.
- Multiple Fractures in RTA (Road Traffic Accident).
- Avascular Necrosis.
- Post Knee or hip replacement prosthesis loosening.
- Polyarthropathy and sacroiliitis.
ENDOCRINOLOGY
Thyroid Scan (Technetium)
- To evaluate palpable thyroid nodule.
- To evaluate thyromegaly & toxic goiters, Gravis Disease, Autonomic Thyroid Nodules.
- To evaluate midline neck swelling.
- Thyroiditis.
- Ectopic Thyroid.
Radio-lodine I – 131 Scan
- In patients with thyroid cancer
- Post operative assessment of remnant thyroid tissue in the neck and visualization of functioning metastasis in the whole body
MIBG Scan
- To detect & localize adrenal / extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma, neuroblastoma & other neuro-endocrine tumors.
NEPHRO-UROLOGY
Tc – 99m DTPA Renal Scan
- Split renal functions.
- GFR estimation.
- Evaluation of hydronephrosis, PUJ Stenosis, VUJ obstruction.
- Renovascular Hypertension
- Transplant evaluation
Tc – 99m DMSA Cortical Scan
- Pyelonephritis
- Chronic and repeated Urinary Tract Infection
- VU Reflux disease
- Ectopic Kidney
Direct Radionuclide Voiding Cyctography (DRCG)
- Detection & follow up of vesico-ureteric reflux
- Repeated Pyelonephritis
CEREBROVASCULAR SYSTEM
Brain SPECT (Tc – 99m ECD)
- Assessment of stroke
- To detect Epileptic focus
- To evaluate dementia
Trodat Scan (Dopamine Receptor Imaging)
- Parkinsonism.
